

LIETUVA
Lietuvių
Lietuvių
Europe
- EUROPE - English
- CZECHIA - Čeština
- DANMARK - Dansk
- DEUTSCHLAND - Deutsch
- ESPAÑA - Español
- FRANCE - Français
- HRVATSKA - Hrvatski
- ITALIA - Italiano
- LATVIJA - Latviešu
- LIETUVA - Lietuvių
- MAGYARORSZÁG - Magyar
- NEDERLAND - Nederlands
- ÖSTERREICH - Deutsch
- POLSKA - Polski
- PORTUGAL - Português
- SCHWEIZ - Deutsch
- SLOVENSKO - Slovenčina
- SLOVENIJA - Slovenščina
- SUOMI - Suomi
- SCHWEIZ - Français
- UK - English
- ΕΛΛΆΔΑ - Ελληνικά
- БЪЛГАРИЯ - Български
- СРБИЈА - Српски
- УКРАЇНА - Українська
- TÜRKIYE - Türkçe
- РОССИЯ - Русский
- БЕЛАРУСЬ - Русский
- О’ZBEKISTON - Русский
- О’ZBEKISTON - O’zbekcha
- ҚАЗАҚСТАН - Қазақ
- ҚАЗАҚСТАН - Русский
Asia
Middle East and North Africa
USA, Latin America



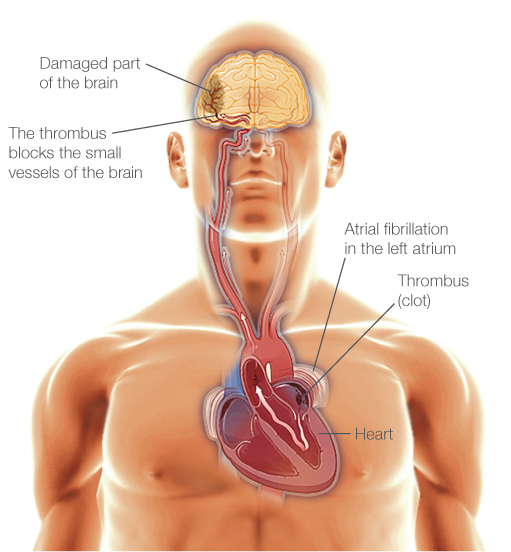 Esant PV, širdis susitraukinėja greitai ir chaotiškai. Dėl to kraujo tėkmė prieširdžiuose sulėtėja, kraujas ima krešėti, formuojasi trombai. Atsiskyrę maži trombai su kraujo tėkme gali patekti į smegenis ir, užkimšę kraujagyslę, sukelti insultą. Labiausiai PV pavojingas dėl to, kad net apie 70% jo epizodų lieka nepastebėti ir nediagnozuoti. Maža to, pradinėse fazėse PV pasireiškia retai ir chaotiškai, todėl ilgą laiką lieka nepastebėti net ir lankantis pas gydytoją. Papildomi faktoriai, didinantys PV atsiradimo riziką: amžius, hipertenzija, diabetas, nutukimas, kardiovaskulinės ligos, stresas, rūkymas ir alkoholis.
Esant PV, širdis susitraukinėja greitai ir chaotiškai. Dėl to kraujo tėkmė prieširdžiuose sulėtėja, kraujas ima krešėti, formuojasi trombai. Atsiskyrę maži trombai su kraujo tėkme gali patekti į smegenis ir, užkimšę kraujagyslę, sukelti insultą. Labiausiai PV pavojingas dėl to, kad net apie 70% jo epizodų lieka nepastebėti ir nediagnozuoti. Maža to, pradinėse fazėse PV pasireiškia retai ir chaotiškai, todėl ilgą laiką lieka nepastebėti net ir lankantis pas gydytoją. Papildomi faktoriai, didinantys PV atsiradimo riziką: amžius, hipertenzija, diabetas, nutukimas, kardiovaskulinės ligos, stresas, rūkymas ir alkoholis.